Jakarta Railway Route Shortest Path with Dijkstra Algorithm
Overview
Have you ever heard the statement "Leetcode is Overrated" or "You probably won't ever use all those complex algorithms and data structures that you learn in those boring lectures"?


My previous experience proves that knowing at least some basic data structure will help your career quite a lot. In this article, I'll elaborate on it!
The App Goal
The app's name is Comute App, a navigation app that mainly focuses on helping deaf people commute by Train in Jakarta, Indonesia area. The app's main function is to
track user location -> generate shortest path route that contains the list of the station that user need to pass -> notify them on certain station (usually transit and end station)
 To achieve the station route most of the time people will look into an API such as Google Maps API or OpenStreetMap, the main problem with them is that:
To achieve the station route most of the time people will look into an API such as Google Maps API or OpenStreetMap, the main problem with them is that:
- it requires network
- probably not free and not cheap either
Hence, I found a workaround which is to calculate the shortest path ourselves using Dijkstra algorithm.
Dijsktra Algorithm
Purpose and Use Cases
With Dijkstra's Algorithm, you can find the shortest path between nodes in a graph. Particularly, you can find the shortest path from a node (called the "source node") to all other nodes in the graph, producing a shortest-path tree.
This algorithm is used in GPS devices to find the shortest path between the current location and the destination. It has broad applications in industry, especially in domains that require modeling networks.
History
This algorithm was created and published by Dr. Edsger W. Dijkstra, a brilliant Dutch computer scientist, and software engineer.
In 1959, he published a 3-page article titled "A note on two problems in connexion with graphs" where he explained his new algorithm.

Dr. Edsger Dijkstra at ETH Zurich in 1994 (image by Andreas F. Borchert) During an interview in 2001, Dr. Dijkstra revealed how and why he designed the algorithm:
What’s the shortest way to travel from Rotterdam to Groningen? It is the algorithm for the shortest path, which I designed in about 20 minutes. One morning I was shopping in Amsterdam with my young fiancée, and tired, we sat down on the café terrace to drink a cup of coffee and I was just thinking about whether I could do this, and I then designed the algorithm for the shortest path. As I said, it was a 20-minute invention. In fact, it was published in 1959, three years later. The publication is still quite nice. One of the reasons that it is so nice was that I designed it without pencil and paper. Without pencil and paper you are almost forced to avoid all >avoidable complexities. Eventually that algorithm became, to my great amazement, one of the cornerstones of my fame
Basic Concept
Graphs are data structures used to represent "connections" between pairs of elements.
- These elements are called nodes. They represent real-life objects, persons, or entities.
- The connections between nodes are called edges.
This is a graphical representation of a graph:
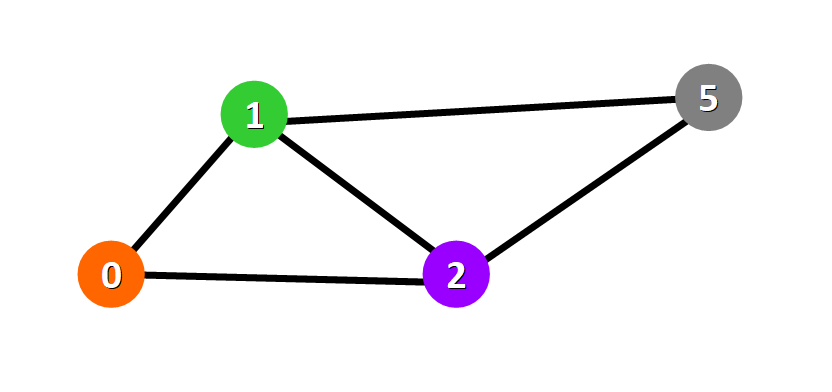
Nodes are represented with colored circles and edges are represented with lines that connect these circles.
Real case graph example:
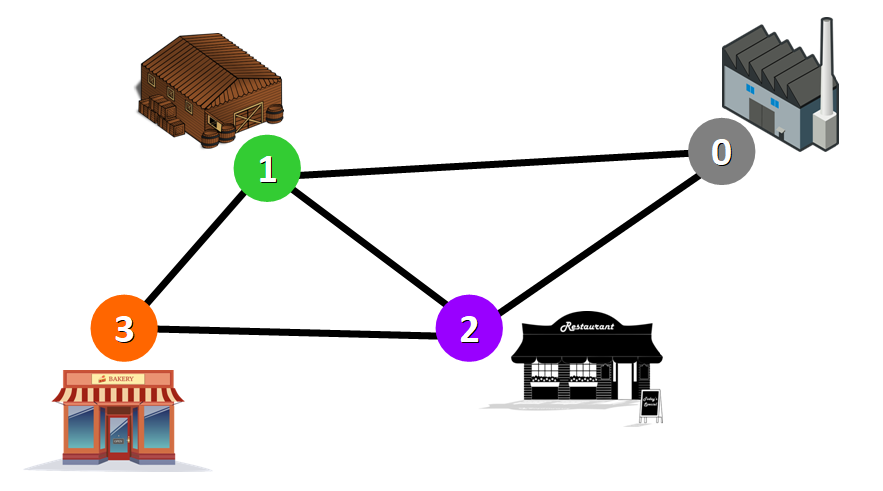
💡 Tip: Two nodes are connected if there is an edge between them.
Easy Explanation
In a summarized way, the algorithm…
- Take a boolean array spt[] and initialize all the elements to 0 (0 = unvisited, 1 = visited).
- Create an array v[], which holds the distance of the nodes from starting node and initialize it to infinity.
- Starts at the node that we give as a parameter and it will return the shortest path between this node and all the other nodes (or vertexes) in the graph.
- It calculates the shortest distance from each node to the source and saves this value if it finds a shorter path that the path that it had saved before. It calculates the distance between a node and the origin node, if this distance is less than it has been saved before, the new minimum distance will be the new distance.
- Once Dijkstra’s algorithm has found the shortest path between the origin node and another node, it marks the node as visited (if it didn’t do it the algorithm could enter into an infinite loop).
- Steps 4 and 5 are repeated until all the nodes are visited. This way, we have visited all the nodes and we’ve saved the shortest path possible to reach each node.
Time Complexity
Dijkstra’s Algorithm Complexity can be vary depending on the implementation, but normaly it is O(n²) being n the number of vertexes. And the space complexity O(n).
Reference:
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/dijkstras-shortest-path-algorithm-visual-introduction/
You can find me on
Twitter: https://twitter.com/mlven23
GitHub: https://github.com/melvnl
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/melvin-liu/
Note: If you have any questions, you can leave a message below by Sign In with your GitHub account 😉